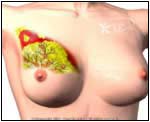
 Normal | 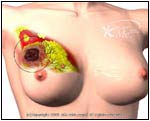  Abnormal |
| |
|
 Normal |   Abnormal |
| |
|

Cramping that is similar to menstrual cramps occurs very early during pregnancy and happens when the uterus begins to expand to make room for the embryo to develop into a fetus that continues to develop for a total of 40 weeks gestation when your baby is born.
Running to the bathroom – During the first trimester of pregnancy, it’s easy to believe you might have to “move” into your bathroom since it seems you are constantly running to make to the bathroom. The growing uterus causes frequent urination during pregnancy. The first and third trimesters of pregnancy are typically when the most intense frequent urination happens.
Headaches – Headaches that occur during pregnancy are often intense and caused by increased hormone levels.
Mood swings – Don’t think you’re crazy if you suddenly develop atypical mood swings or if you are unusually emotional during pregnancy, these are very normal reactions during pregnancy. Many times, pregnant women burst into tears for reasons that are unclear to anyone, including the pregnant woman. Another symptom caused by increased hormone levels.
Increased basal body temperature or BBT – Your basal body temperature is your temperature immediately upon rising in the morning. BBT normally increases during ovulation and decreases when menstruation occurs. However, when pregnancy takes place increased basal body temperature continues after menstruation is late. BBT is a good indicator of pregnancy for women who have used it, either to prevent pregnancy or when trying to get pregnant.
Children born to mothers who smoke experience more colds, ear aches, respiratory problems, and illnesses requiring visits to the pediatrician than children born to nonsmokers.
The fact is women smokers have around 72 percent of the fertility of nonsmokers. When all other factors are equal, it is 3.4 times more likely that smokers will require over one year to conceive.
Increasingly, studies are showing that decreased ovulatory response, as well as the fertilization and implantation of the zygote may be impaired in women who smoke. Thought is also given that chemicals in tobacco may alter the cervical fluid, making it toxic to sperm causing pregnancy to be difficult to achieve.
We can't leave the men out on this one, though. Men smokers are 50 percent more likely to become impotent. Some of the toxic chemicals found in cigarettes may result in gene mutations that can cause miscarriage, birth defects, cancer, and other health problems in their children.
Menstrual problems such as abnormal bleeding, amenorrhea (absence of periods), and vaginal discharges/infections are common complaints among women who smoke.
Menstrual abnormalities and early menopause may be caused by a toxic effect on the ovaries or by the significantly lower levels of estrogens noted in many studies of women smokers.
The good news is that if you quit now your potential risk of dying as a result of future breast cancer remains the same as for a nonsmoker.
If your partner refuses to wear a condom, insist that you talk about it. Explain what you know about safe sexual behavior and condom use. If your partner feels uncomfortable buying the condoms, then you can offer to buy them. In the end, if he refuses to wear a condom, you should be concerned, and reconsider the relationship.
It can be difficult to talk about using condoms, but you shouldn't let embarrassment become a health risk. The person you are thinking about having sex with may not agree at first when you say that you want to try and use a condom when you have sex. These are some excuses that might be made and some answers that you could try:
| EXCUSE | ANSWER |
| Don't you trust me? | Trust isn't the point, people can have infections without realising it |
| I can't feel a thing when I wear a condom | Maybe that way you'll last even longer and that will make up for it |
| I don't stay hard when I put on a condom | I'll help you put it on, that will help you keep it |
| I don't have a condom with me | I do |
| I'm on the pill, you don't need a condom | I'd like to use it anyway. It will help to protect us from infections we may not realise we have. |
| But I love you | Then you'll help us to protect ourselves. |
| Just this once | Once is all it takes |
During the monthly menstrual cycle, female sex hormones prepare the uterus to support a pregnancy. If pregnancy takes place, menstruation usually does not return until after childbirth. If pregnancy does not occur, the endometrial lining (the lining of the uterus) sheds during menstruation. Menstrual blood and tissues leave the body through the vagina and it usually lasts from three to seven days.
Treatment
Treatment for abnormal menstrual will depend on many factors, including the cause, your age, the severity of the bleeding, and whether you want to have children. Treatments include use of birth control pills or hormones, hysteroscopic removal of polyps or fibroids, endometrial ablation, and hysterectomy.
Hormones
Your doctor may prescribe birth control pills to help your periods to be more regular. They also may improve other symptoms. Progesterone can help prevent and treat endometrial hyperplasia (abnormal thickening of the lining of the uterus).
Other Medications
Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, like ibuprofen and naproxen, may help control heavy bleeding.
Surgery
Some women with abnormal menstrual bleeding may need to have surgery to remove growths (such as polyps or fibroids) that are causing the bleeding.
Endometrial ablation also is used to treat abnormal menstrual bleeding. Resection of the lining of the uterus, ablating it with cautery, or heating the inside of the uterus to close the blood vessels shut are excellent minimally invasive procedures to control abnormal uterine bleeding.
Hysterectomy, or the removal of the uterus, is another procedure that may be used to treat abnormal vaginal bleeding. This can be accomplished laparoscopically with very small incisions on your abdomen. This can also be done in the traditional "open" manner with a large abdominal incision. For those with pre-cancerous or cancerous change, a hysterectomy is standard. A hysterectomy is a major surgery.
Finally ...
If you notice that your menstrual cycles have become irregular, see your doctor. Abnormal bleeding has a number of causes. There is no way of telling why your bleeding is abnormal until your doctor examines you. Once the cause is found, abnormal bleeding often can be treated with great success using minimally invasive procedures in an outpatient or office setting.
How do you know when bleeding during your period is abnormally heavy? The easiest way to know if you are experiencing menorrhagia is to take note of how often you need to change your pad or tampon. If your period is heavy enough to require changing more often than every one or two hours, or if you have a period that lasts more than a full week, you may be experiencing menorrhagia.
Let’s take a look at the most common causes of menorrhagia or heavy menstrual bleeding:
1.A hormonal imbalance during adolescence or menopause is the most common cause of heavy menstrual bleeding.
Ipill, an emergency contraceptive pill, is gaining popularity among teenagers, despite of repeated warning from doctors aginst its use.Ipill as suggested by doctors is only proved for women aged from 25-45.
“Because it’s an over the counter product, one doesn’t need a prescription,” says Rahul Arora of Inder Medicos, Safdarjung. The trend, says Atul Shah of Atul Medicos, Karol Bagh, is more prevalent among the affluent class. “But it’s bound to spread,” says RS Gupta of Paras Chemist, Saket. An industry official says, “The iPill is meant for women aged 25 to 45. Chemists should not sell it to youngsters.”
"It can be potentially harmfull",cautions gynaecologist Dr Rita Baksh," since it is a hormonal pill".Frequent use can cause ovarian damage and menstrual problems, especially among younger girls, she adds.
Certain side effects as mentioned by ISARC reserchers include, reduced sex interest, skin allergies and lose of vigour.Long time effects of a hormonal pill cant be predicted.Continues use may reduce the chances of future pregnency too.
You can't miss the hi voltage campaign Cipla has unleashed for its product. What's interesting is how safe the advertiser has kept his communication. Husbands and wives, birth control and family planning. You know - we Indians have sex only when married and more so use contraception because producing another child into this world would mean additional burden to the nation.
OK, seriously, words like 'family planning' disappeared from our vocabulary approximately two decades ago, along with slogans like 'hum do, hamara do'. The inverted red triangle which was everywhere you turned when I was a kid has been banished.
Heck, we're no longer ashamed of our billion plus population but flaunt is as a dhinchakly large consumer market.
But getting back to the i-pill you can see why the advertiser is treading soo..o cautiously. He wouldn't want to be accused of corrupting our Indian youth and so on and so forth.
Indian Express reports:
As the revelries of Navratri draw closer, condom once again has become the bad word. While the NGOs working for AIDS control are steering clear from condom promotion programmes that they usually launch during the festival, the Bajrang Dal has said it will not tolerate any condom promotion or HIV/AIDS awareness programmes around Garba venues this time.
Talking to Newsline, an NGO worker, on the condition of anonymity, said they used to put up stalls at various Garba venues to create public awareness about HIV/ AIDS. This time, however, they will not do so, he added.
“Last time, some activists claiming to represent the Hindus, had beaten up NGO workers in Baroda during Navratri while they were distributing condoms,” the NGO worker said, adding that they have decided against carrying out overt intervention programmes this season. “We will carry out one-on-one intervention programmes instead, and supply condoms to hotels and guesthouses” he said.
Wonder whether the dals will stake out these venues as well!
According to a pharmacist quoted in the report, "sale of condoms rise by about 70 per cent during Navratri". And this year I am sure the I-pill will rock as
well.
"After iPod, I-pill gains popularity with youth", says Midday:
Alka Kumar, a consulting gynecologist at Gurunanak hospital in Bandra, says, “This product is a boon for married women not planning to conceive. But it may be misused by the youth especially during Navratri when unmarried pregnancies go up.”
The reason for all the action around Navratri is related more to opportunity than anything else. A lot of young people, esp girls, are allowed to stay out late. Dressed in sensuous chaniya cholis and whirring to the dandiya beat , hormones are bound to get into a tizzy. Pehle hota tha, ab bhi hoga. Instead of a botched abortion, many a young woman will opt for an i-pill.
But the two messages "prevention of pregnancy" and "prevention of HIV/ sexually transmitted diseases" have become independent of each other. The i-Pill can help with the first bit but do nothing for the second.
It would be terrible if young people decide to adopt the convenient route: Condom nahi hai? Koi baat nahin - you can always use the i-Pill. So let's go ahead anyways.
That's not what the advertiser has intended, but I bet a lot of folks will interpret it that way. If we accept that the i-Pill will be used by unmarried guys and girls, we can address this issue.But hello, yeh hai India. We will have to continue the charade and keep promoting 'family planning'.
Why not bring back the red triangle as well? Dunno - it just makes me nostalgic :)
It's a product targeted at her 38-year-old mother. But it’s 16-year-old Pihu Vohra (name changed) who is using the widely advertised emergency contraceptive Intelligent Pill, or iPill, that can prevent pregnancy if taken within 72 hours of having ‘unsafe’ sex. 2 weeks ago